Does cardiac action potential have repolarization?
- Does cardiac action potential have repolarization?
- What is repolarization cardiac?
- What are the phases of the cardiac action potential?
- Does repolarization mean contraction?
- Is repolarization contraction or relaxation?
- What are the 4 stages of action potential?
- How many action potentials do pacemaker cells have?
Does cardiac action potential have repolarization?
Phase 1—Transient Outward Current. Phase 1 of the cardiac AP is the transient and relatively small repolarization phase that immediately follows the upstroke of the AP. The size of phase 1 repolarization varies between species and also between different regions of the heart within a given species.
What is repolarization cardiac?
What is meant by depolarization of the heart? Depolarization of the heart is the orderly passage of electrical current sequentially through the heart muscle, changing it, cell by cell, from the resting polarized state to the depolarized state until the entire heart is depolarized.
What happens in repolarization stage?
Repolarization is a stage of an action potential in which the cell experiences a decrease of voltage due to the efflux of potassium (K+) ions along its electrochemical gradient. This phase occurs after the cell reaches its highest voltage from depolarization.
What causes the repolarization phase of cardiac muscle action potentials?
Repolarization (phase 3 of the action potential) occurs because of an increase in potassium permeability. At the SA node, potassium permeability can be further enhanced by vagal stimulation. This has the effect of hyperpolarizing the cell and reducing the rate of firing.
What are the 5 phases of cardiac action potential?
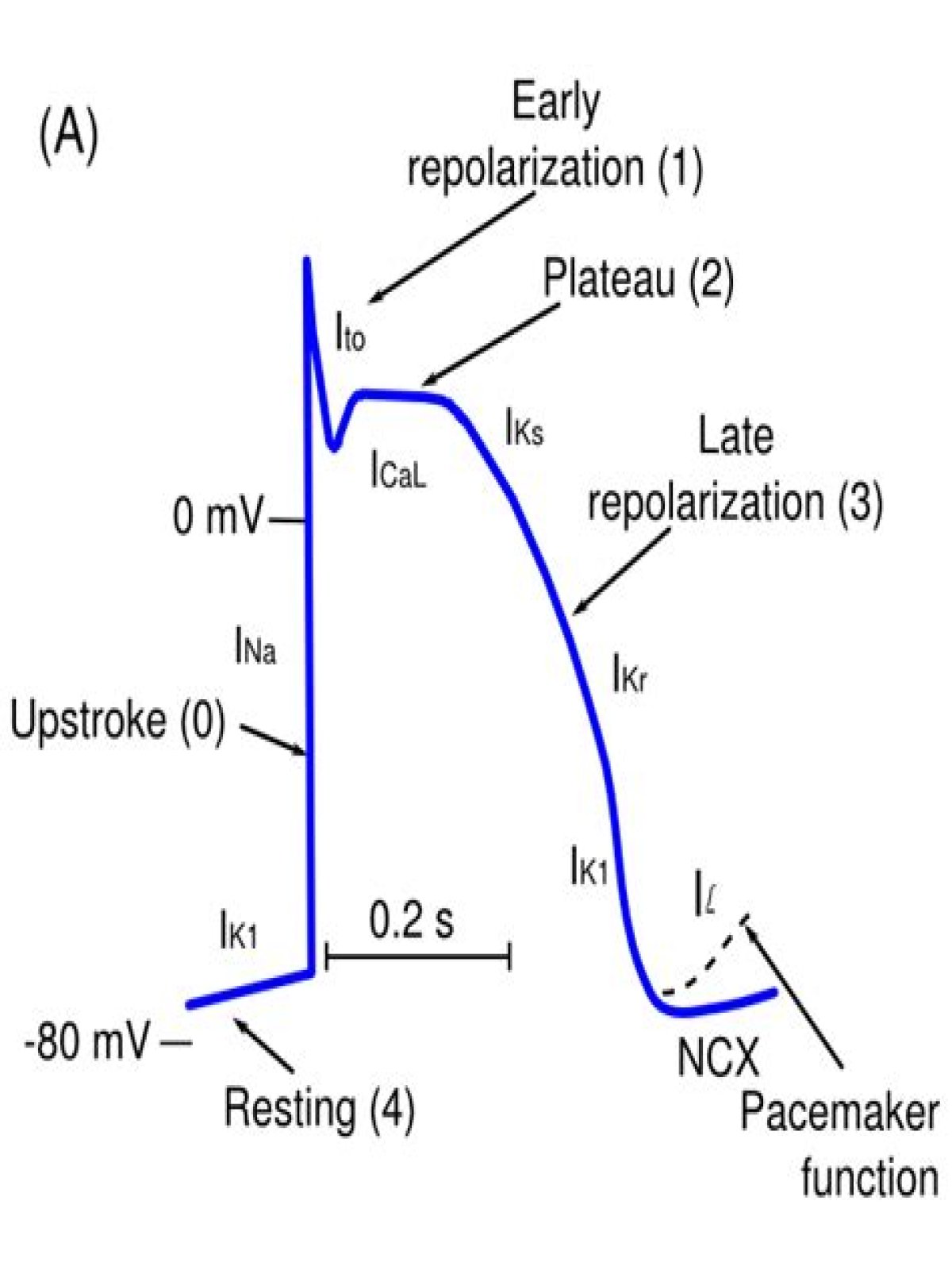
Membrane currents that generate the a normal action potential. Resting (4), upstroke (0), early repolarization (1), plateau (2), and final repolarization are the 5 phases of the action potential.
What are the phases of the cardiac action potential?
The action potential in typical cardiomyocytes is composed of 5 phases (0-4), beginning and ending with phase 4.
- Phase 4: The resting phase.
- Phase 0: Depolarization.
- Phase 1: Early repolarization.
- Phase 2: The plateau phase.
- Phase 3: Repolarization.
Does repolarization mean contraction?
In muscle cells, the action potential causes a muscle contraction. Depolarization and repolarization of the entire heart can be measured on the skin surface. Depolarization of the heart leads to the contraction of the heart muscles and therefore an EKG is an indirect indicator of heart muscle contraction.
What is cardiac action potential?
The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage (membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells. All cardiac muscle cells are electrically linked to one another, by structures known as gap junctions (see below) which allow the action potential to pass from one cell to the next.
What are the 4 steps of an action potential?
An action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. It consists of four phases: depolarization, overshoot, and repolarization.
What are the 5 steps of an action potential?
The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase.
Is repolarization contraction or relaxation?
When the electrical signal of a depolarization reaches the contractile cells, they contract. When the repolarization signal reaches the myocardial cells, they relax.
What are the 4 stages of action potential?
An action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. It consists of four phases: depolarization, overshoot, and repolarization. An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button.
Why do calcium channels remain open during cardiac action potentials?
The calcium channels remain open and the potassium efflux is eventually balanced by the calcium influx. This keeps the membrane potential relatively stable for about 200 msec resulting in the PLATEAU phase, characteristic of cardiac action potentials.
What happens during the rising phase of the action potential?
This results in the rising phase. At peak, potassium channels open, calcium channels inactivate, potassium ions leave the cell and the voltage returns to -60mV. This is falling phase of the action potential.
What is the depolarizing phase of a sodium channel?
This is the depolarizing phase. L-type, or SLOW, calcium channels also open at -40mV, causing a slow but steady influx. Sodium channels close quickly, voltage-gated potassium channels open and these result in a small decrease in membrane potential, known as EARLY RE-polarization phase.
How many action potentials do pacemaker cells have?
Pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes exhibit different forms of action potentials. The pacemaker cells of the SA node SPONTANEOUSLY fire about 80 action potentials per minute, each of which sets off a heartbeat. Pacemaker cells do NOT have a TRUE RESTING potential.